Magnesium Glycinate vs Citrate: Understanding the Differences and Benefits

Introduction to Magnesium Supplements
Magnesium Glycinate vs Citrate, Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in several physiological processes within the human body. It is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions, including those that regulate muscle and nerve function, maintain blood sugar levels, and support the production of protein, bone, and DNA. As a vital nutrient, magnesium must be consumed regularly through diet or supplements, as the body cannot adequately produce it on its own.
While magnesium can be obtained from various food sources, such as green leafy vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, many individuals may find it challenging to meet their daily requirements. This gap has led to a widespread increase in the usage of magnesium supplements, which come in different forms. Among these, magnesium glycinate and magnesium citrate are two popular options that consumers often consider.
Magnesium glycinate is a compound formed by combining magnesium with glycine, an amino acid. This form is known for its high bioavailability, meaning that it is easily absorbed in the digestive tract. As a result, magnesium glycinate is often recommended for those seeking to correct magnesium deficiency without experiencing gastrointestinal distress.
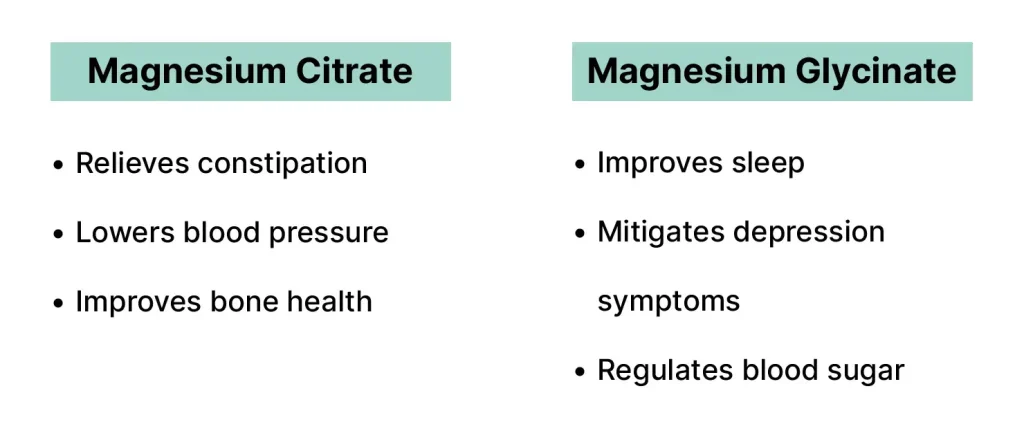
In contrast, magnesium citrate is magnesium combined with citric acid. It is also well-absorbed and is known for its laxative effects, making it beneficial for those dealing with constipation. This form is often utilized not only for replenishing magnesium levels but also for its additional digestive benefits.
As more individuals turn to magnesium supplements to enhance their health, understanding the differences and benefits of magnesium glycinate vs citrate is essential in making informed choices regarding supplementation. In this blog post, we will delve deeper into these two forms of magnesium, their unique properties, and the potential benefits they offer to consumers.
What is Magnesium Glycinate?
Magnesium glycinate is a compound formed from magnesium and glycine, an amino acid known for its calming effects. This combination creates a chelated form of magnesium, which significantly enhances its absorption compared to other forms of magnesium supplements. When consumed, magnesium glycinate is less likely to cause gastrointestinal discomfort than compounds like magnesium oxide or citrate, making it a preferred choice for many individuals seeking magnesium supplementation.
The principal benefit of magnesium glycinate lies in its ability to provide a highly bioavailable source of magnesium. Bioavailability refers to the degree and rate at which a substance is absorbed into the bloodstream, and magnesium glycinate excels in this regard. Studies indicate that this form of magnesium can effectively increase magnesium levels in the body, leading to various health benefits, including improved muscle function, better sleep quality, and enhanced mood stability. As magnesium is crucial for diverse metabolic functions, its supplementation is often recommended for those experiencing deficiencies.
Potential side effects of magnesium glycinate are generally mild, especially when compared to other forms of magnesium. Some individuals may experience stomach upset or diarrhea, but such occurrences are less frequent. It is typically considered safe for most people and is often cited as suitable for long-term use. Those who suffer from conditions that deplete magnesium levels, such as chronic stress, fibromyalgia, or gastrointestinal issues, might find magnesium glycinate particularly beneficial. Overall, it is a versatile supplement that can play a significant role in promoting optimal health when taken as directed.
What is Magnesium Citrate?
Magnesium citrate is a compound formed by combining magnesium with citric acid. This creates a highly soluble form of magnesium that is readily absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, which is one of the primary reasons it is widely regarded as a beneficial dietary supplement. Being one of the more bioavailable forms of magnesium, magnesium citrate is often used to address magnesium deficiencies and promote overall health within the body.
The absorption of magnesium citrate in the body occurs mainly in the small intestine, where it dissolves and is taken up into the bloodstream. Its high solubility ensures that it is less likely to cause gastrointestinal discomfort, a common side effect associated with other forms of magnesium. This advantageous absorption profile makes magnesium citrate particularly appealing for individuals who may struggle with constipation, as it can help to initiate bowel movements due to its osmotic effect in the intestines.
There are several health benefits attributed to magnesium citrate, including its role in regulating muscle and nerve function, blood sugar levels, and blood pressure. Furthermore, it aids in the synthesis of protein, bone development, and the production of DNA and RNA. Many people use magnesium citrate as a dietary supplement to improve digestive health and alleviate conditions such as migraines, muscle cramps, and anxiety. However, potential drawbacks include a possible laxative effect, especially when taken in higher doses, which may not be suitable for everyone.
In specific scenarios, magnesium citrate may be particularly beneficial for athletes or individuals engaged in regular physical activity. It can help replenish magnesium levels after exercise through its efficient absorption. As with any supplement, it is prudent for individuals to consult with healthcare professionals to understand the appropriate use and implications of magnesium citrate, ensuring it aligns with their specific health needs and conditions.
Comparative Analysis: Magnesium Glycinate vs Citrate
When examining magnesium glycinate vs citrate, one can observe essential differences in their characteristics, including absorption rates, bioavailability, digestive tolerance, and potential side effects. Understanding these factors can aid individuals in making informed decisions regarding which supplement is best suited for their needs.
To begin with, absorption rates play a crucial role in how effectively these compounds deliver magnesium to the body. Magnesium citrate is known for its higher solubility in water, making it generally more bioavailable compared to magnesium glycinate. This characteristic allows magnesium citrate to be absorbed more rapidly into the bloodstream. However, those who require a gentler option might find magnesium glycinate to be more suitable, as it tends to have a slower absorption process which may reduce the risk of digestive discomfort.
Bioavailability is another critical factor in evaluating these two forms of magnesium. Magnesium glycinate is often considered better tolerated by the gastrointestinal tract. This compound is chelated with glycine, an amino acid that aids in absorption and minimizes potential laxative effects. Conversely, magnesium citrate, while effective, may cause diarrhea or other digestive issues in sensitive individuals, especially when taken in higher doses.
Additionally, considering potential side effects is important. Magnesium glycinate generally has a lower incidence of adverse reactions, making it ideal for people with digestive sensitivities or for those who are aiming for long-term supplementation. In contrast, magnesium citrate may lead to gastrointestinal disturbances if excessive amounts are consumed, which might deter some users.
Ultimately, the choice between magnesium glycinate and citrate requires careful consideration of individual health needs, lifestyle, and any pre-existing conditions. Each form offers distinct advantages, thereby highlighting the importance of understanding magnesium glycinate vs citrate to ensure optimal dietary supplementation.
Health Benefits of Magnesium Glycinate
Magnesium glycinate is a highly bioavailable compound that combines magnesium with the amino acid glycine. This unique pairing enhances the absorption of magnesium in the body, making it an effective choice for individuals seeking to increase their magnesium levels. One notable health benefit of magnesium glycinate is its ability to promote relaxation. Research indicates that magnesium plays a crucial role in regulating neurotransmitters, which are vital for managing stress and instilling a sense of calm. As a result, many users report feeling more relaxed when including this supplement in their daily regimen.
Improving sleep quality is another significant benefit of magnesium glycinate. Studies have linked magnesium deficiency to sleep disturbances, and supplementing with this form of magnesium may help improve overall sleep quality. By assisting in the regulation of melatonin, the hormone responsible for sleep cycles, magnesium glycinate may help individuals fall asleep faster and enjoy deeper sleep. Many people have shared positive experiences regarding better sleep patterns after incorporating magnesium glycinate into their nightly routine.
Additionally, magnesium glycinate has been recognized for its potential to reduce anxiety. Anecdotal evidence suggests that individuals suffering from anxiety disorders have experienced relief after taking this supplement. The calming effects of glycine may complement magnesium’s benefits, creating a synergistic effect that promotes emotional well-being.
Moreover, magnesium glycinate aids in muscle recovery, which is particularly beneficial for athletes and fitness enthusiasts. The compound helps mitigate muscle cramps and spasms, often resulting from intense workouts or physical exertion. By supporting muscle function and recovery, magnesium glycinate ensures that individuals can maintain their physical activity levels without discomfort.
In conclusion, magnesium glycinate offers a wide range of health benefits, including relaxation, improved sleep quality, anxiety reduction, and enhanced muscle recovery, making it a practical choice for individuals seeking to optimize their well-being.
Also Read Siliconsift.co.uk
Health Benefits of Magnesium Citrate
Magnesium citrate is a highly bioavailable form of magnesium that offers various health benefits. One of its most recognized uses is as a natural remedy for constipation. By attracting water into the intestines, magnesium citrate helps to soften stools, making bowel movements easier and more regular. Studies have shown that individuals suffering from occasional constipation often find significant relief after taking magnesium citrate supplements, highlighting its effectiveness and safety as a laxative alternative.
In addition to its role in digestive health, magnesium citrate also plays a crucial part in maintaining electrolyte balance within the body. Electrolytes are essential for many physiological functions, including muscle contractions and nerve signaling. Magnesium citrate helps regulate the levels of other electrolytes such as calcium and potassium, thereby supporting overall hydration and preventing conditions like muscle cramps and fatigue. This balance is particularly important for athletes and individuals engaging in rigorous physical activities, where electrolyte loss can occur rapidly.
Furthermore, magnesium citrate has been linked to supporting cardiovascular health. Research indicates that adequate magnesium levels can help manage blood pressure and promote better heart function. Magnesium citrate may contribute to the relaxation of blood vessels, leading to reduced resistance and lower blood pressure levels. This effect is beneficial for individuals at risk of heart disease or those looking to improve their heart health. Testimonials from users underscore the positive impact of magnesium citrate on their wellness, often noting improvements in blood pressure readings and overall cardiovascular performance.
Overall, magnesium citrate presents a versatile approach for enhancing health, addressing constipation, maintaining electrolyte balance, and promoting heart health. This makes it a valuable addition to one’s dietary regimen, especially for those seeking the unique advantages it offers compared to other forms of magnesium.
Potential Side Effects of Each Supplement
When considering magnesium supplements, it is essential to understand the potential side effects associated with magnesium glycinate and magnesium citrate. Both forms are known for their bioavailability and effectiveness, yet they exhibit different safety profiles that merit discussion.
Magnesium glycinate is generally well-tolerated, primarily due to its chelated form, which allows for easier absorption and minimal gastrointestinal disturbance. However, individuals might experience mild side effects, including diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal discomfort, particularly if taken in excessive doses. As a rule of thumb, it is advisable not to exceed the recommended daily intake unless directed by a healthcare professional. Additionally, those with renal impairment should exercise caution, as impaired kidney function can lead to magnesium accumulation in the body.
On the other hand, magnesium citrate may have a more pronounced laxative effect, making it potentially unsuitable for individuals with sensitive digestive systems or preexisting gastrointestinal conditions. Side effects can also include cramping, diarrhea, and dehydration when taken excessively. As with magnesium glycinate, individuals with compromised kidney function should consult a healthcare provider before use, as the risk of hypermagnesemia, which is an elevated magnesium level in the blood, is increased in this group.
Interactions with medications are another aspect to consider. Magnesium glycinate can interact with certain antibiotics and medications for osteoporosis, reducing their effectiveness. Similar interactions are noted with magnesium citrate, particularly with medications that require optimal magnesium levels for proper absorption. Therefore, it is advisable to space out the intake of magnesium supplements and other medications. Ultimately, understanding the potential side effects of magnesium glycinate vs citrate can assist consumers in making informed decisions regarding their supplementation needs.
How to Choose Between Glycinate and Citrate
When considering magnesium supplementation, particularly in the forms of magnesium glycinate vs citrate, it is essential to assess several factors that can guide your decision. Firstly, personal health goals play a significant role. Magnesium glycinate is often favored for its superior absorption and calming effects, making it ideal for individuals seeking to improve sleep quality or manage anxiety. In contrast, magnesium citrate is more commonly utilized for digestive support, as it can aid in alleviating constipation due to its mild laxative properties.
Another crucial factor is existing health conditions. Individuals with digestive sensitivities might prefer magnesium glycinate, as it is generally easier on the stomach and less likely to cause gastrointestinal discomfort. Conversely, those who specifically need a supplement that promotes bowel regularity may consider magnesium citrate, which can be more effective in this regard. Therefore, it is vital to evaluate your specific health needs and choose the formulation that aligns with them.
Tolerance to supplements also varies among individuals. Some may find that they tolerate one form of magnesium better than the other. Therefore, it may be beneficial to start with lower doses and monitor how your body reacts to either magnesium glycinate or citrate. If side effects arise, it may be necessary to switch formulations accordingly. Furthermore, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable, as they can provide tailored recommendations based on your unique health profile and wellness objectives.
In summary, the choice between magnesium glycinate vs citrate hinges on personal health goals, existing health conditions, tolerance to different supplement forms, and professional medical advice. By carefully considering these factors, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their magnesium supplementation.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Decision
In the discussion of magnesium glycinate vs citrate, it is essential to emphasize the distinct properties and potential benefits associated with each form. Magnesium glycinate is often favored for its superior bioavailability and the lower risk of gastrointestinal side effects, making it a popular choice for those who seek to support overall health, particularly in relation to stress and sleep quality. On the other hand, magnesium citrate may be more beneficial for individuals who are looking to alleviate constipation and require a more immediate laxative effect, due to its ability to increase water content in the intestines.
As we consider the unique aspects of magnesium glycinate and citrate, one must also take personal health needs into account. Individual factors such as existing medical conditions, concurrent medications, and specific health goals should guide the selection process. It is crucial for potential users to be aware of their personal tolerance levels and objectives when choosing between these two forms of magnesium supplementation.
Before embarking on any new dietary or supplement regimen, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide valuable insights and tailor recommendations based on individual health circumstances. This is especially important in the context of magnesium supplementation, as excessive intake can sometimes lead to adverse effects. By making informed decisions, individuals can effectively harness the benefits of magnesium supplements to enhance their well-being. In summary, understanding the differences between magnesium glycinate vs citrate allows for a more educated choice that aligns with one’s health aspirations.